From the mid-1900 the world completely turned against dietary fat leaving its benefits up in the air. The evolution of our ancestors started with fat consumption, and at that time there were no cardiac arrests or metabolic syndrome-related diseases. My personal experience and clients’ practice of consuming fat-dominant foods have shown great results in improved metabolism, energy levels, and sleep quality. It is a great source of fuel that our bodies can use. Among the 3 macronutrients Protein, carbohydrates, and fat, fat provides thrice the amount of ATP than the other two macros. 1 gram of fat provides 147 moles of ATP (energy currency that our body uses) compared to 1 gm of glucose (which is only 37 moles of ATP). In general, the fat oxidation-adapted body showed great results in sustaining the activity for a prolonged period without any ingestion of glucose in middle intervals like long-distance running, swimming, and cycling in various studies.
Well before getting into our topic, I would like to explain the types of lipids or fats. These are organic compounds and are soluble in organic solvents not in water. These are broadly classified into 1. Simple, 2. compound, and 3. derived.
Simple lipids are divided into triglycerides and waxes. The TGLs are nothing but a combination of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids. In our diet, we consume 96 percent of fat as triglycerides. While waxes are the sticky substance like a honeycomb, ear wax, etc.,
Fatty acids are then categorized into two types based on their chemical composition which are namely saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids. To get a better understanding of this, we studied that carbon’s atomic number is 6 and to attain stability it can combine with 4 other atoms. If you see the chemical structure of a saturated fatty acid. The carbon atoms are stable because it does not contain a double bond in their carbon chain chemical structure and are not reactive in the environment when subjected to heat. Sources of saturated fatty acids are 1. Ghee 2. Coconut oil 3. Butter, cheese, animal fat, etc.
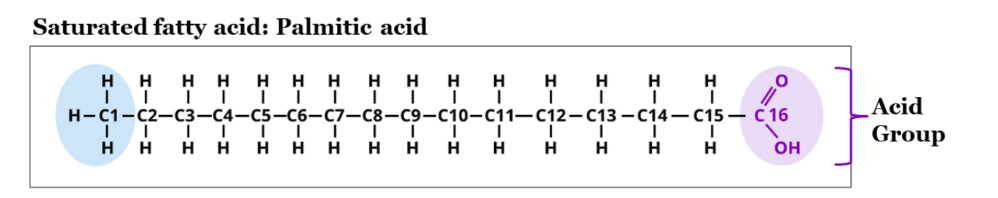
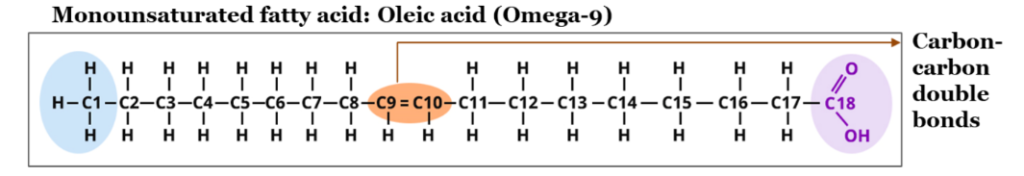
Unsaturated fatty acids are those having the structure of one or more double bonds in their carbon chain, making them unstable when subjected to heat. Based on the placement of double bonds these are bifurcated into monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
In a mono-unsaturated fatty acid, it has only one double bond between the 9th and 10th carbon atoms from the omega/carboxylic end. Since it contains only 1 double bond in its carbon chain it is termed a Monounsaturated fatty acid. Sources with high concentrations of Mono-unsaturated fatty acids are Olive, Peanut, canola, avocados, etc.
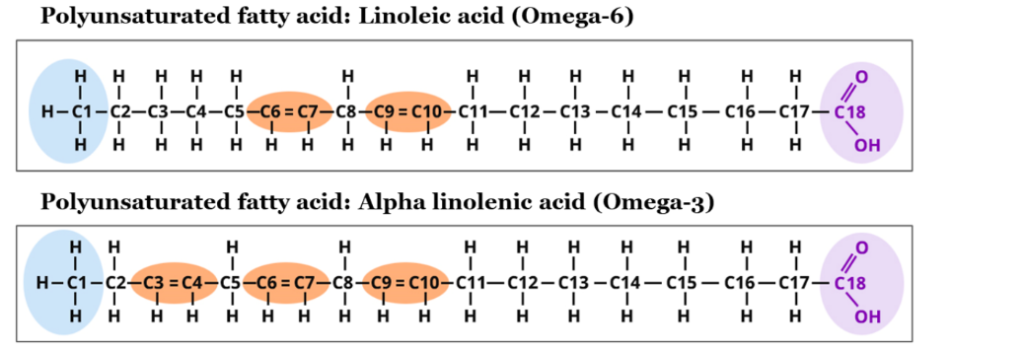
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are classified into omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids. As the name poly depicts many, these are the fatty acids having 2 or more than 2 double bonds in their carbon chain. If the 1st double bond exists between the 3rd and 4th carbon atoms from the omega end, it is Omega-3 fatty acid. Similarly, if the double bond exists between the 6th and 7th carbon atoms, it is known as Omega-6 fatty acid.
The sources having high concentrations of Poly-unsaturated fatty acids are sunflower oil, flax seed oil, corn, safflower, soybean oil, etc.
Now, in our daily life, the majority of people knowingly or unknowingly use oils that are in peak concentrations of unsaturated fatty acids. We have seen that a fatty acid with a weak link in its carbon chain is highly reactive with oxygen in the environment to regain stability. Unfortunately, oxidized fatty acids are dangerous to our health. The causes of chronic usage of these are obesity, low immune response, high inflammation, and imbalance in lipid profile in plasma resulting in cardiovascular issues and many more.
In a more practical way, we know that coconut oil or ghee melts and converts into the oil. After keeping them at a low temperature for a while, they attain their earlier state without changing their color. It means its chemical composition is undisturbed. On the other hand, take any oil that is extracted from seeds or nuts, after a certain time of heating them at pan temperature, we can address a change in color of the oil, because of its reaction with oxygen available in the environment.
Compound lipids diversified into phospholipids and glycolipids. Phospholipids serve a vital purpose in the body as bilayers of the cell membrane. The phospholipids function of semi-permeability of the cell wall, protecting against the intrusion of foreign bodies. Phospholipids are one of them which fall under the category of essential fatty acids. There is a direct connection between dietary fat ingestion to the quality of cell membrane maintained, hence it is recommended to add saturated fatty acids to the diet to aid the purposefulness.
Derived lipids originate from both simple and compound lipids by means of hydrolysis. Bile acids, cholesterol, sex hormones, etc. According to research, people having low dietary cholesterol in their food, have been reported in low levels of testosterone. This can be the potential cause of fat gain in adult males with no cholesterol intake leading to low testosterone levels compared to estrogen levels in the body.
It is believed that eating dietary cholesterol tends to produce greater production of circulating cholesterol namely low-density lipoprotein and causes arterial occlusions. It is a part of the cell membrane. Cholesterol is extremely essential for human survival. It helps in myelinating the neural axons which help in insulating the axon for greater electric impulse transmissions. Sex and stress hormones are produced by cholesterol only.
Cell integrity is maintained for selective permeability of nutrients and minerals. I know that the answer still remains unclear about an arterial blockage. For a better understanding, I would like to use an analogy for better understanding. At every fire accident we notice the fire brigade, and that does not mean the fire brigade is the cause of that fire accident.
The root cause of endothelial cell damage is chronic elevation of insulin and imbalance lipid profile in the plasma. To work on endothelial cells, macrophages get deposited as an immune response. In the same way, circulating cholesterol gets plagued and starts piling up along with macrophages reducing the lumen diameter of blood vessels.
Another significant function of cholesterol is myelinating the nerve axons for insulation. Well-insulated nerve fibers are more efficient in transferring electric potential. Thus benefitting the improved cognition performance and efficient physical movements.
It is believed that eating dietary cholesterol tends to produce greater production of circulating cholesterol namely low-density lipoprotein and causes arterial occlusions. It is a part of the cell membrane. Cholesterol is extremely essential for human survival. It helps in myelinating the neural axons which help in insulating the axon for greater electric impulse transmissions. Sex and stress hormones are produced by cholesterol only. Cell integrity is maintained for selective permeability of nutrients and minerals.
I know that the answer still remains unclear about an arterial blockage. For a better understanding, I would like to use an analogy for better understanding. At every fire accident we notice the fire brigade, and that does not mean the fire brigade is the cause of that fire accident. The root cause of endothelial cell damage is chronic elevation of insulin and imbalance lipid profile in the plasma. To work on endothelial cells, macrophages get deposited as an immune response. In the same way, circulating cholesterol gets plagued and starts piling up along with macrophages reducing the lumen diameter of blood vessels.
Resources:
Inflammatory Mechanisms of Diabetes and Its Vascular Complications (nih.gov)
